 Trainable parameters for the learnable geometric scattering network
Trainable parameters for the learnable geometric scattering networkAbstract
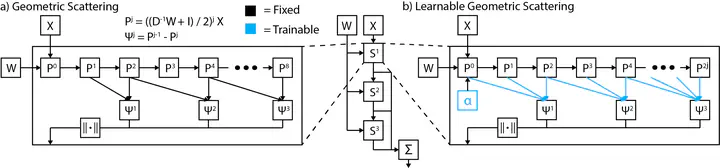
Graph neural networks (GNNs) in general, and graph convolutional networks (GCN) in particular, often rely on low-pass graph filters to incorporate geometric information in the form of local smoothness over neighboring nodes. While this approach performs well on a surprising number of standard benchmarks, the efficacy of such models does not translate consistently to more complex domains, such as graph data in the biochemistry domain. We argue that these more complex domains require priors that encourage learning of band-pass and high-pass features rather than oversmoothed signals of standard GCN architectures. Here, we propose an alternative GNN architecture, based on a relaxation of recently proposed geometric scattering transforms, which consists of a cascade of graph wavelet filters. Our learned geometric scattering (LEGS) architecture adaptively tunes these wavelets and their scales to encourage band-pass features to emerge in learned representations. This results in a simplified GNN with significantly fewer learned parameters compared to competing methods. We demonstrate the predictive performance of our method on several biochemistry graph classification benchmarks, as well as the descriptive quality of its learned features in biochemical graph data exploration tasks. Our results show that the proposed LEGS network matches or outperforms popular GNNs, as well as the original geometric scattering construction, while also retaining certain mathematical properties of its handcrafted (nonlearned) design.
Also presented at ML4M Workshop @ NeurIPS 2020